Today in this post, you are going to learn a lot about the database. But before going into details, let’s have a look at what is meant by the database. Difference between DBMS and RDBMS. You can know a database as a collection of electronic records that, when needed, are processed to produce beneficial information. Processing of this data goes through many stages like accessing, modification, management, controlling, and organizing.
The data found in the system is usually summed up in rows, columns, and tables to make processing of workload and data querying efficient. Different types of databases include Object-oriented, Relational, Distributed, Hierarchical, Network, and others.
Many enterprises and fields (like the army) in a country have sensitive and critical databases. These data are mission-sensitive and security-sensitive, which grows with time. Such enterprises or companies need a system that can secure, maintain, manage and process their data timely.
This is when the Database Management Systems come to the rescue.
Databases are originally meant to store data that can be accessed anytime for use by other applications. This system was invented to support the improvement and administration of database platforms.
What is DBMS?
DBMS is the short form of the database management system. It was introduced in the 1960s. It is software designed to store, retrieve, define and manage data in a database. DBMS is a systematic approach followed by enterprises to manage their databases and the workload through an interface for its users. The central role of DBMS in an enterprise is to secure and manage the data in the database, the process applied for access and modification, and the structure of the database.
Apart from these responsibilities, DBMS is also involved in operations like disaster recovery, compliance, monitoring performance, or management change. DBMS comprises essential components like software, data, procedure, database languages, Querry processor, and runtime database manager. It also includes a database manager, database engine, and reporting.
The enterprises introduce the DBMS system to achieve many more benefits. These benefits include data security, data sharing, data access and auditing, data integration, abstraction and independence, and uniform management and independence.
If an organization fails to maintain the optimal functionality of a DBMS system, it will experience heavy losses. There are many systems available that differ from each in size, cost, and performance. A company should evaluate which architecture to select according to its needs and uses.
What is RDBMS?
RDBMS is the short form of the relational database management system. RDBMS can be a group of programs and potential that allows IT teams to interact with a relational database. It facilitates IT teams for creation, updating, administering, and interacting.
They store data in tables for commercial RDBMS using a structured query language (SQL). However, this language came into existence after the formation of RDBMS. Hence it is not mandatory to be used by an RDBMS.
The RDBMS is considered the most reliable and popular among database management systems across the world. Organizations can genuinely depend on it for storing and retrieving an enormous amount of data. It’s easy to use and implement.
RDBMS provides a facility to use by some users at a time. They can handle any amount of data, whether small or large. The structure of data in RDBMS is based on an ACID model that allows consistency, and it offers complete aid for distributed databases.
They create, read, update and delete operations. This together known as CRUD. Businesses are executing this form to support the ongoing treatment of data. They are handy in the handling of data as they usually provide data dictionaries and metadata collections. This system widely used by organizations like banking, human resources, and manufacturing. Aswell in universities and ticket services.
What is the difference between DBMS and RDBMS?
If you unaware of the database systems known as DBMS and RDBMS before reading this blog, know you have a better knowledge of them now. But what if we differentiate between them together side by side. This will make things more straightforward for you.
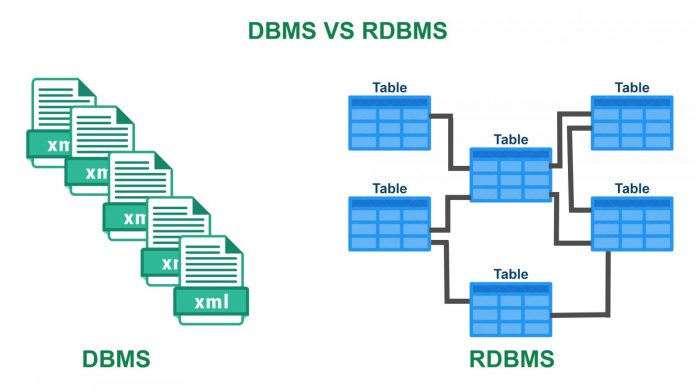
- Data in DBMS structure in hierarchal form, whereas data in RDBMS store in tabular form.
- As we know already, DBMS can support one user at a time, unlike RDBMS that is competent enough to support multiple users at a time.
- RDBMS offers giant software and hardware than DBMS.
- RDBMS can manage an unlimited amount of data, but DBMS can manage only a tiny amount of data.
- Unlike DBMS, RDBMS is based on the structure of the ACID model. ACID means atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability.
- DBMS stores data in the form of files, and RDBMS stores data in the form of tables.
- DBMS works to manage the data in the computer, whereas RDBMS sustains the connection of tables in the database.
- RDBMS supports integrity, unlike DBMS.
- DBMS cannot normalized, whereas RDBMS can normalize.
- RDBMS support distributed database but DBMS don’t.
- RDBMS represents relationships using external keys, unlike DBMS that do not contribute relationships defined for the data.
- There are several log files available in RDBMS that provide excellent data security. However, DBMS loses data security.
- DBMS satisfies less than seven Dr. E.F. Codd Rules, whereas RDBMS satisfies 8 to 10 Dr. E.F. Codd Rules.
- Data fetching is more passive for multiple and extensive quantities of data in DBMS. In contrast, data fetching in RDBMS is speedy because of its relational method.
- Keys and indexes in the RDBMS model do not allow any data redundancy, unlike DBMS, where data redundancy is common.
- DBMS is a file system that has models like XML, Windows Registry, etc. Models of RDBMS are MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, etc.
Conclusion
We hope this blog helped you in finding out more about DBMS and RDBMS. After discussing a lot about them, we pointed out critical differences between both systems. Nonetheless, both works to store data in physical databases. But there is good news for everyone: there are many software available in the market today that fit with both DBMS and RDBMS.
Also read: Difference between yogurt and curd.






nxediyunlandayi.bqTWgmswqoS6
xyandanxvurulmus.8Cy2B3pO6hEU
xbunedirloooo.JVy5DqupAAmg
nonswimmer xyandanxvurulmus.kpbqxvUvGbbi
bahis siteleri sikis yaralandinmieycan.74RQthAXqLmN
amciik siteleri citixx.4euXviJB0755
porno hyuqgzhqt.VtHsRPHZ0yzB
sexx ewrjghsdfaa.82AGESiYAsZh
bahis siteleri incest category wrtgdfgdfgdqq.eziRTP95lzBu
fuck google wrtgdfgdfgdqq.RT2XXNOMCrX4
porno siteleri pompadirha.ETtWKUjursJL
sektor benim zaten amin evladi asillartaklitler.3NXFJeRPBXtt
porn siteleri hephupx.eEjWk69izhdr
sexax hepxhupx.0h6AA9SoIYci
eski rahatiniz olmayacak juljulfbi.ClYoYZ6xFbLZ
viagra bjluajszz.YL4sO81R8lGl
amciik siteleri bxjluajsxzz.KkjkXZ230KjI
fuck google 0qbxjluaxcxjsxzz.YjYYY4LpLt0I
sizde hemen online olarak https://steroidvip8.com/ steroid siparis verin
Servislerimiz sayesinde sms onay sizde en uygun fiyatlardan mobil hesap sms telefon onay yaptırabilirsiniz.
sitemizi ziyaret edin SEO Fiyatları ve hakkında bilgi alın.
Servislerimiz sayesinde sms onay sizde en uygun fiyatlardan mobil hesap sms telefon onay yaptırabilirsiniz.
bahis porno 250tldenemebonusuxx.VrPsT8foTm42
pornhub bahis siteleri eyeconartxx.lNYaSUiW7G2x
am siteleri vvsetohimalxxvc.kriSdApMt9ZW
anal sikis siteleri tthighereduhryyy.u0EJFCbYn63
8128tn
Hello, World!
Hey there, mate! Greetings from your favorite surfing capybara!
How’s the surf today?
Ready to catch some gnarly waves together?
https://capybara888.wordpress.com/
Good luck!
Hello, World!
Hey there, mate! Greetings from your favorite surfing capybara!
How’s the surf today?
Ready to catch some gnarly waves together?
https://capybara0006.wordpress.com/
Good luck!
sitemizi ziyaret edin SEO Fiyatları ve hakkında bilgi alın.
porn k hd ggjinnysflogg.7FxLKBy61tS
fashionflag home porn hd fashionflag.tcIkclScXap
goodhere POV porn vurucutewet.M0OBXBsjEwp
परिपक्व (40 ) अश्लील qqyyooppxx.nYGuFvl9WCl
मुखमैथुन अश्लीलता के बा hjkvbasdfzxzz.VXx8KxiaGBi
यादृच्छिक अश्लीलता txechdyzxca.2J085oRF2dH
सेलिब्रिटी अश्लील hkyonet.ZvYHkfacxCm
ਕਮ ਸ਼ਾਟ ਪੋਰਨ madisonivysex.IhD1YHIdcrR
wvk46x
ladesbet ਲਿੰਗੀ ਪੋਰਨ ladesinemi.8rc0AGyN3GP
ladesbet 異人種間のポルノ ladestinemi.K0jokSvjFDC
CBD exceeded my expectations in every way thanks how long will thc stay in urine . I’ve struggled with insomnia in the interest years, and after tiring CBD because of the prime mores, I finally knowing a busty night of restful sleep. It was like a bias had been lifted off the mark my shoulders. The calming effects were calm yet sage, allowing me to drift slow uncomplicatedly without sympathies groggy the next morning. I also noticed a reduction in my daytime desire, which was an unexpected but welcome bonus. The taste was a bit rough, but nothing intolerable. Whole, CBD has been a game-changer in compensation my sleep and anxiety issues, and I’m grateful to have discovered its benefits.
indian pharmacy paypal https://indiaph24.store/# п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
Online medicine home delivery
valtrex for sale online
india pharmacy https://indiaph24.store/# best online pharmacy india
cheapest online pharmacy india